
Division of Technical Resources (DTR) Office of the Director (OD)
Leads the conduct of
Scientific Bioenvironmental Research to resolve technical issues of an unusual scope and difficulty to advance emerging scientific technologies used in the design of federal biomedical research facilities. The results of these studies have often been adopted as national and international standards for biomedical laboratories and healthcare facilities.
Manages and operates the
Bethesda Campus Central Utility Plant (CUP), the
Cogeneration Plant and the
NIH Utility Distribution System (except electrical distribution) in accordance with the State of Maryland environmental standards to ensure that utilities are delivered safely and efficiently.
Manages utility and energy contracts and purchases, and validates steam and electricity bills for the Bethesda Campus in the interest of maintaining the public trust.
Leads advanced computational analysis and mathematical models to improve biomedical environments; develops energy forecasting models to reduce energy consumption while improving indoor air quality in biomedical laboratories, animal research and health care facilities; and employs numerical modeling and trend analysis strategies to facilitate purchasing decisions that maximize cost savings using an
Artificial Neural Network (ANN) in conjunction with Holt-Winter triple exponential smoothing that takes into account seasonal and trend changes.
DTR Technical Support Branch (TSB)
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) plays a pivotal role in advancing biomedical research, necessitating the construction and renovation of specialized laboratories and facilities. Through the DTR Permit Review process, the Technical Support Branch (TSB) provides comprehensive design reviews to ensure compliance with all applicable regulations, codes, and standards. TSB provides engineering technical expertise, quality assurance (QA), and oversight of design and construction documents associated with the design and construction of Biosafety Level (BSL) 2, 3, and 4 biomedical research facilities, animal research facilities, aseptic production facilities (APF), healthcare facilities, data centers, and the NIH Central Utility Plant (CUP). TSB is comprised of the major engineering disciplines (Architectural, Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing, Civil and Structural). By fostering a cross-functional and collaborative environment amongst NIH Project Officers (PO), project designers and NIH stakeholders, TSB aims to ensure all design projects meet the rigorous benchmarks for code, safety, efficiency, and effectiveness, ultimately contributing to the broader mission of public health and scientific discovery.

Ensures the NIH facility design and construction conform to all applicable regulations, codes and standards, policies, and guidelines including: ASHRAE, FGI, FDA, ANSI, ICC, NFPA, ANSI, ASME and the NIH Design Requirements Manual (DRM).
Responsible for DRM revisions that pertains to the respective TSB engineering disciplines.
Conducts studies of unusual scope, highly complex and technical nature for emerging technologies and trends that are applied to the design of NIH facilities through the DRM and other codes and standards.
Coordinates design and construction reviews in consultation with appropriate NIH divisions, branches and institutions (e.g., DDCM, DTSB, DFOM, DFS, DEP, ORS, DOHS, DRS, and DFM) to ensure comprehensive engineering and cost-effective design solutions to meet the end-user's project objectives.
In 2024, TSB personnel conducted 887 Design Reviews from 348 Design Submissions across the NIH construction portfolio and responded to 85 Variance Requests to the DRM.
DTR Facilities Compliance and Inspection Branch
(FCIB)
FCIB plays critical role in ensuring the safety, regulatory compliance, and operational integrity of the NIH's Aseptic Processing Facilities (APF). Our work not only ensures that the APF program meets the highest standards of regulatory compliance but also protects the health and well-being of patients, researchers, and staff. With a focus on precision, safety, and efficiency, FCIB is a key part of NIH's operational success and regulatory stewardship in the production of life-saving biomedical products. As an integral part of the NIH's mission, FCIB provides comprehensive quality assurance oversight across the entire lifecycle of the APF program, from design and construction to commissioning, validation, turnover, operations, and ongoing maintenance. Our work supports the production of therapeutic, diagnostic, and research products, including pharmaceuticals, radiopharmaceuticals, and biologics for human use.
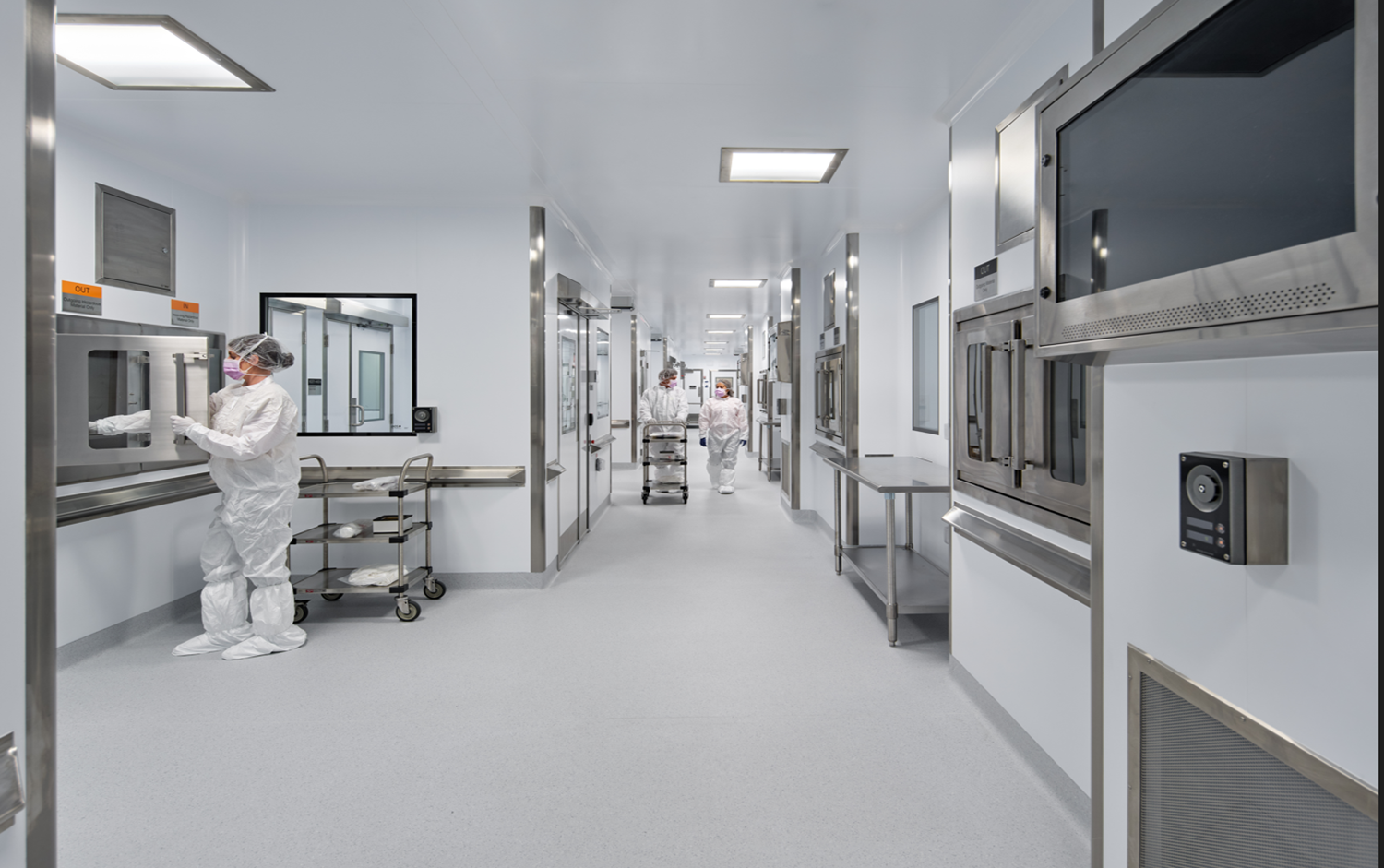

Our Core Responsibilities Include:
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance: We oversee compliance with all relevant regulatory standards, guidelines, and current industry best practices to maintain facilities in a state of control. This minimizes risk and ensures adherence to essential safety protocols for both patients and workers.
Promoting Safety and Risk Mitigation: By implementing rigorous monitoring systems and ensuring all processes are aligned with safety regulations, we reduce risks to patients, staff, and the environment. Our oversight of the facilities and their critical environmental parameters, coupled with ongoing performance evaluations, safeguards against operational risks.
Enhancing Facility Performance and Accountability: We provide robust quality assurance oversight of the Division of Facility Operations and Maintenance (DFOM) and its role in supporting APF facilities. Through careful deviation management, workplan reviews, and internal audits, we ensure that operational procedures remain flawless and continuously meet regulatory requirements.
Facilitating Change Management: We manage the Change Management Board (CMB) for the APF program, ensuring that all facility modifications undergo thorough reviews to assess regulatory, engineering, and operational impacts. This process includes identifying and mitigating any risks associated with facility changes, further protecting the integrity of the facilities and their critical functions.
FCIB has been the cornerstone of the demonstrated quality and performance of the APF facility program and is currently working with various stakeholders to provide similar services and capabilities to the BSL-3 portfolio.
DTR Standards and Policy Branch (SPB)
Develops and maintains ORF technical policies and standards for the design, construction, commissioning, operations, and maintenance of NIH facilities. These are documented in the Design Requirements Manual , technical publications, and Standards Operating Procedures (SOPs), which set the standard for the safety, efficiency, and reliability of NIH owned, leased, operated, and funded buildings and facilities. Technical policies and standards are based on best practices, ever-advancing architectural and engineering technologies, and studies conducted at the NIH.

Manages and updates the NIH Design Requirements Manual (DRM), which provides detailed design requirements and criteria for NIH owned, leased, operated, and funded buildings and facilities. DRM requirements and criteria maintain the high standard of safety, efficiency, and reliability of state-of-the-art research facilities.
Manages the DTR Permit Review process, which provides comprehensive design reviews for all NIH-funded facilities and issues permits for construction. The Permit Review process provides technical expertise, quality assurance, and oversight of design and construction documents, and ensures compliance with the DRM and applicable regulations, codes, and standards. The Permit Review process ensures facility safety, efficiency, and effectiveness, ultimately contributing to the broader mission of public health and scientific discovery. Permit Review Flow Chart.
Provides architectural and related technical expertise, including consultation, DRM interpretation and variance approvals, reviews of design documents, and other services for DRM updates, publications, boards, committees, and individual design and construction projects.
Develops technical publications such as News to Use and NIH Technical Bulletins to provide news of technological advancements, best practices, and DRM updates to assist in the design and delivery of the highest quality facilities. Publications are distributed electronically to over 11,000 readers, including the designers, operator, and users of research facilities.
Manages the ORF Technical Library, which provides ORF architects, engineers, and Project Officers access to the latest codes, standards, and relevant technical publications.


Maintains and manages International Association for Continuing Education and Training (IACET) certification for technical and professional continuing education in ORF. IACET is an internationally-recognized organization dedicated to setting the highest possible standards for continuing education and training. The ANSI/IACET Standard is the backbone of leading educational programs worldwide, and IACET Accredited Providers are the only organizations approved to offer IACET Continuing Education Units (CEUs).
In order to earn Accredited Provider status, DTR completed a rigorous application process in 2010, which included a review by an IACET site visitor, and successfully demonstrated adherence to the ANSI/IACET 1-2007 Standard regarding the design, development, administration, and evaluation of its programs. The program has since maintained its Accredited Provider status by submitting a comprehensive reaccreditation application once every five years; as of the most recent reaccreditation, the DTR Training Program is compliant with the current ANSI/IACET 1-2018 Standard.
DTR Data Science and Artificial Intelligence Application Branch (DSAIAB)
DSAIAB
is a modern Machine Learning Operations (MLOps), Development Operations (DevOps),
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD), and Agile project
management embracing group DTR. DSAIAB is dedicated to increasing efficiency,
ensuring data security and integrity, and empowering resilience and proactive
decision-making across all DTR branches.
Our Mission and Capabilities
Advanced Data Platform:
Data Collection and Processing: Our platform collects over 500 million daily data points and performs approximately 1 million advanced calculations per day to support DTR's decision-making processes.
Optimization: We employ artificial neural networks, gradient-boosted models, Bayesian optimization, and other machine learning/artificial intelligence-based software packages to generate over 175,000 data points per day for approximately 12,500 constrained variables, optimizing operations for NIH's Aseptic Facilities and the Central Utility Plant (CUP).
Technological Integration:
MLOps and DevOps: We integrate MLOps and DevOps practices to streamline machine learning workflows, enhance collaboration between development and operations teams, and ensure robust model deployment and monitoring.
CI/CD: Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines are utilized to automate testing, integration, and deployment processes, enabling frequent and reliable software releases.
Agile Project Management:
Methodologies: We utilize Agile project management methodologies to manage projects with flexibility and continuous feedback, ensuring iterative improvements and rapid adaptation to changing requirements.
Team Collaboration: Agile practices facilitate enhanced collaboration among cross-functional teams, promoting transparency, accountability, and efficient project delivery.
Software Development:
Angular and Python: Our team is proficient in developing responsive web applications using Angular and robust backend systems using Python, particularly with frameworks like Django. This full-stack development approach ensures seamless and efficient software solutions tailored to our operational needs.
Cybersecurity:
Comprehensive Security Measures: DSAIAB is committed to ensuring robust cybersecurity across all systems, adhering to NIST.SP.800-82r3 standards for SCADA systems. We conduct periodic risk assessments, IT audits, and vulnerability management to safeguard data integrity and system security.
System Support: We support over 30 custom applications, ensuring they meet stringent cybersecurity requirements and operational standards.
Cloud Migration:
On-Premises to Azure: We are actively migrating from on-premises to cloud-hosted development and deployment to embrace the scalability and versatility of Microsoft Azure. This transition enhances our ability to scale operations, improve performance, and leverage Azure's robust suite of tools and services.
Generative AI:
Vector Indexing and Graph Databases: We utilize generative AI techniques with vector indexing and graph databases to provide grounded, context-aware responses, enhancing the accuracy and relevance of our data-driven insights.
Advanced Analytics:
Data Governance:
Framework Implementation: DSAIAB implements a comprehensive Data Governance framework that defines data management practices for the entire data lifecycle, ensuring the availability, consistency, trustworthiness, usability, integrity, and security of all enterprise data.

![]()
NIH Central Utility Plant (CUP)
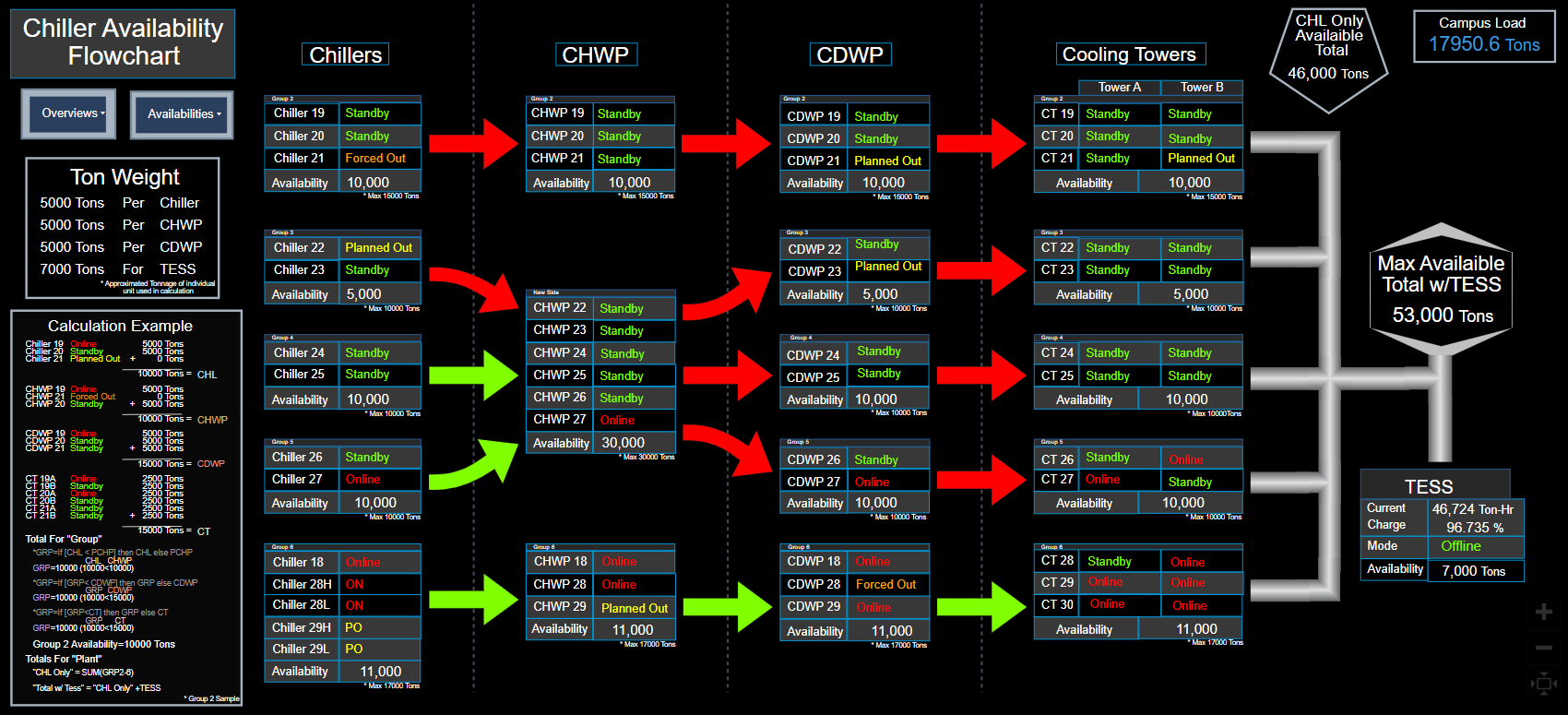
| 
|
Ensures that the Bethesda campus CUP and central utility distribution system (except electrical distribution) operate reliably and in accordance with the State of Maryland environmental standards by providing engineering-based expertise, strategies, and oversight of CUP and facility maintenance operations to ensure continuous, efficient, and optimal plant performance;
Conducts formal root-cause analyses of non-normal CUP operating conditions and system failures;
Develops corrective action plans and ensures that the solutions receive timely attention and required funding;
Oversees design activities, condition assessments, construction, and commissioning activities in the central plant;
Conducts and coordinates short- and long-term major buildings and facilities planning analyses and forecasting models to meet facility planning requirements;
Develops and oversees standards of performance for utility operations and maintenance contract work;
Manages utility contracts and purchasing;
Validates steam and electrical bills;
Develops energy conservation measures for the power plant;
Develops technical SOPs and manuals to ensure efficient system operations and energy conservation; and
Reviews project plans and designs for compatibility with existing systems and consistency with future facility development plans.
Utilities Generation Branch (UGB)
Operates the Bethesda campus CUP in accordance with the State of Maryland environmental standards. The UGB oversees the physical, mechanical, and electrical maintenance of all CUP systems related to the generation of chilled water, steam, and compressed air, as well as other utility systems pertaining to the central plant. UGB has two sections: the COGEN Plant Section (CPS) and the Utilities Maintenance Section (UMS).
-
COGEN Plant Section (CPS)
Calibrates, operates, and maintains one of the largest U.S. government
cogeneration plants, which is also one of the cleanest cogeneration systems in the world. The CPS, through its constant vigilance, enables the NIH to effectively and economically meet National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS). The CPS purchases natural gas using financial analyses and hedging strategies that save the NIH millions of dollars annually; and negotiates sophisticated and unique contracts with utility providers. The CPS conducts routine emissions tests; conducts formal root-cause analyses and ensures that the solutions receive timely attention and required funding; creates high-performance solutions to energy inefficiency; conducts risk assessments related to mechanical failures and energy utilization; oversees upgrades to the CUP and associated systems; and procures and oversees the delivery of portable boiler units when required.
Utilities Maintenance Section
(UMS)

UMS is the hub for calibrating and maintaining all digital controls and monitoring equipment; and works in conjunction with the
DSAIAB to review the controls that optimize plant
operation to ensure that the boilers match established performance curves. The UMS develops and revises the standard operating procedures for the CUP functions and oversees programming issues and start-up logic of new controls to optimize 24/7 operations. The UMS is responsible for performing preventive, predictive, and corrective maintenance on a scheduled and emergency basis of all CUP systems.
Utilities Distribution Branch
(UDB)

Operates and maintains the Bethesda Campus central utility distribution systems (except electrical distribution) in accordance with established safety practices and the State of Maryland environmental standards. The UDB monitors all distribution systems related to the CUP to ensure that utilities are delivered safely, efficiently, and optimally; provides communications and coordination with outside utility providers; and oversees all maintenance of utility distribution systems related to the power plant. In addition, the UDB is responsible for:
Coordinating with Building Unit personnel to ensure buildings are shut down safely for maintenance purposes.
Monitoring utility construction projects to ensure that projects meet design and functional needs.
Responding to utility emergencies and restoring services as quickly as possible.
Long-term planning for utility related projects that will replace aging infrastructure.
Coordinating with the Master Planning Department on future growth needs of the NIH campus to ensure adequate utility services.
Providing drawing review for projects that affect utility distribution or for new connections to the distribution system.
Utilities Systems Design and Technical Services Branch (USDTSB)
Provides architectural, engineering and construction management services required for planning, designing, acquiring, constructing, altering, renovating, improving and repairing utility systems and other types of facility projects, as needed. Provides program and project planning advice and consultation during project formulation stage including the production of project concepts, schedules, estimates and programs of requirements. USDTSB is also responsible for monitoring and reporting on progress of projects against approved programs of requirements, budgets, and schedules.
Responsible for managing projects under its purview to successful completion by implementing project controls and risk management strategies to minimize variance from approved programs of requirements, budgets, and schedules. Keeps customers from the NIH community fully involved and informed on the project schedules, costs, and
progress.
Download the Adobe Acrobat Reader plug-in.